AWS Outposts allows you to extend the AWS infrastructure to your on-premises location, offering a consistent hybrid cloud experience. One of the key decisions when setting up your Outposts rack is choosing between two routing modes: CoIP (Customer-Owned IP) and Direct VPC routing.
Direct VPC routing and Customer-owned IP pool are two options for establishing connectivity between your Outpost services and the on-premises network. Both of these solutions are mutually incompatible, and routing works differently depending on which strategy you choose. The two modes are properties of the LGW route table with which your Outpost subnets' VPC is associated, and they define the Outpost subnets' communication method. We'll look at the differences between these modes in this section.
AWS Outposts CoIP mode allows you to bring your own On-premises IP address range to utilize it with your on-premises environment. This allows you to extend your existing IP addressing scheme onto the AWS Cloud while maintaining consistency and familiar network parameters.
When you use CoIP mode, you need to provide a different IP address range from your on-premises IP space so that AWS can construct from an address pool known as a CoIP. When an Outpost-based resource, such as an EC2 instance, an Application Load Balancer (ALB), or an Amazon Relational Database Service (Amazon RDS) instance, requires communication with your on-premises network, the Local Gateway performs one-to-one NAT from the AWS resource private IP address from the Outpost subnet range to an IP address from the CoIP pool.
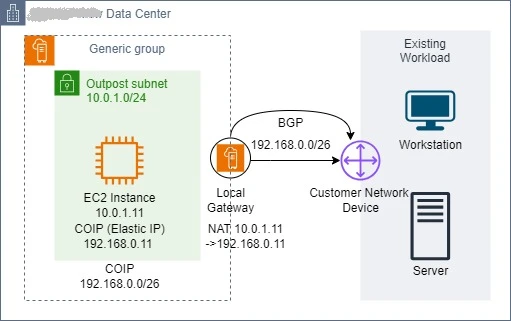
In the above diagram, when the instance Y wants to communicate with an on-premises server, the traffic traverses through the LGW and the source private IP address (10.0.1.11) of the instance gets transalted to an CoIP address (192.168.0.11) that is associated with the instance. Similarly, when the on-premises service initiates the communication with the instance Y, the request will be routed to the CoIP address (192.168.0.11) of the instance as the destination IP address. And this CoIP will be translated to instance's private IP address(10.0.1.11) using managed NAT of CoIP mode at the LGW and this route for CoIP pool (192.168.0.0/26) is advertiesd by BGP to the Customer Network Device in on-premise for reaching the Outpost.
To communicate with your on-premises network, direct VPC routing uses the private IP addresses of the instances in the VPC CIDR block. Border Gateway Protocol (BGP) is used to advertise these addresses to your on-premises network. Advertisement via BGP is only available for private IP addresses that belong to subnets on your Outpost and have a route to the LGW in the subnet's route table. Outposts Rack's default routing mode is this one. The LGW does not execute Network Address Translation (NAT) for instances in this mode. So, in order to communicate with your on-premises resources we do not need to provide an Elastic IP address to th Outpost resources (EC2) from a pool of CoIP.
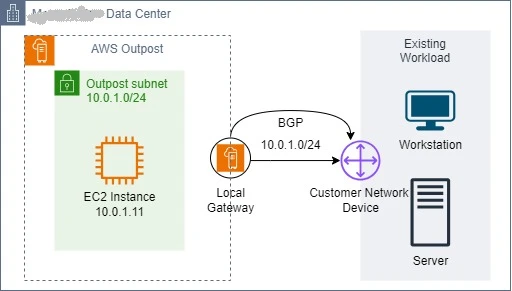
In the above diagram, when the instance Y wants to communicate with an on-premises server, the traffic traverses the LGW and faciliate communication with the on-premises server using its private IP address (10.0.1.11) as the source and similarly when the on-premise server wants to communicate with the instance Y, it uses the instance’s private IP address (10.0.1.11) as the destination IP address to set up the connection.
We can choose between Direct VPC routing or CoIP mode for routing from Outpost to on-premise. Because this option affects the routing for all subnets on your Outpost that are associated with the LGW route table, it should be well planned and chosen based on your workload requirements and existing IP infrastructure design. Later on, you can modify the LGW route table mode. However, this requires network disturbance and the reconfiguration of a LGW route table.


