Introduction to Kubernetes
The software industry is rapidly using containers as a way to
facilitate development, deployment, and environment
orchestration for Application Developers. When it comes to the
deployment of the application to the Kubernetes Cluster, It
becomes very complicated and tedious task. Continuous
Integration and Continuous Deployment is the principle of
DevOps which can be used for Kubernetes application
deployment.
This explains how easy you can set up CI/CD for Kubernetes
cluster by using following components:
- Local Development Environment.
- CI Tools. (Gitlab, Github, etc.)
- CD Tools. (Jenkins, etc.)
- Container Registry. (AWS ECR, Gitlab Registry, etc.)
-
Kubernetes Cluster. (AWS EKS, On-Premise Kubernetes Cluster,
etc.)
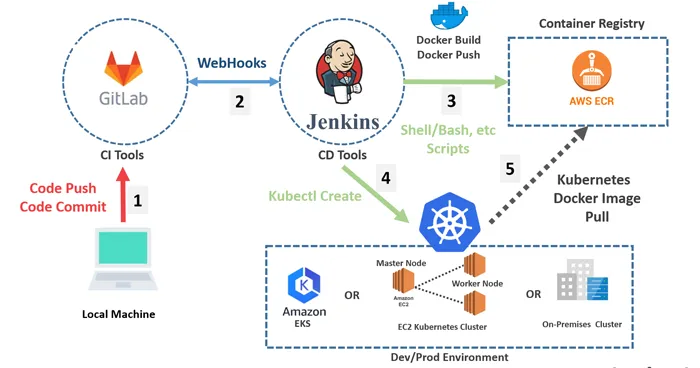
Kubernetes CI/CD Architecture
What is Continuous Integration ?
Continuous Integration is a development practice used by the
developers, where each developer integrates the code into a
shared repository frequently. Each integration can be verified
by an automated build and automated tests using CI Tools.
Developer push and commit the code to a shared/central
repository.
What is Continuous Deployment ?
Continuous deployment is a strategy for software releases.
where the code, which is committed by the developer passes an
automated build and automated testing phase, is automatically
released into the production environment, making changes that
are visible to the software's users.
Steps involved in Kubernetes CI/CD
Create Production ready Application Service
Setup CI Repository
-
Create and configure shared repository for Continuous Push,
Commit, etc.Here we are using Gitlab as shared repository.
Setup CD Tool
-
Install and configure continuous deployment tools for
automatic build and test. Builds are created from the Build
management scripts, written inside Build Configuration. Here
we are using Jenkins as CD Tool.
Setup Container Registry
-
Create central container registry such as AWS EKS or Gitlab
Registry Service. CD Tools will push the container image to
the central container registry.
Create Kubernetes Cluster
-
Development K8S Cluster: Use development support environment
for creating Kubernetes Cluster. Eg : Minikube.
-
Cloud Native K8S Cluster Services: Use Cloud Services to
create Kubernetes Cluster. Eg : AWS EKS Service.
-
On-Premise K8S Cluster: Create your own Kubernetes Cluster
with the help of master and worker nodes.
Working
- Push and commit the code to the Gitlab repository.
-
Gitlab repository will run the webhook. Webhook is the
Jenkins url hit by Gitlab when it has new push.
-
Jenkins will understand that Gitlab has new code and it will
take the code from Gitlab and run the Build Script or Test
Scripts.
-
Jenkins will first create the docker image for application
and then it will be pushed to the Container Registry.
-
Jenkins will run second task as updating Kubernetes
Development Pod Image.
Advantages
- Rapid Deployment.
- Task Automation. Eg: Updating pod,etc.
Disadvantage
-
Kubernetes CI/CD process does not guarantee that your
current processes are fully served while updating the pod
image.
Eg: Consider backend service is serving to the request made
by frontend application. Backend services will take up to 3
min to process the request, within that time period if
developer push any new code then backend service will
terminate all the current serving requests and update the
pod image.
Conclusion
We understand that Kubernetes rolling deployment is very easy
with the help of CI/CD. We also acknowledged that while
updating new pod image, the current requests are terminated.



